搜索到
463
篇与
的结果
-
 React - 事件绑定 1. 基础事件绑定语法:on + 事件名称 = { 事件处理方法/函数 }function App() { const clickHandler = () => { alert('事件绑定') } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={clickHandler}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 2. 使用事件对象参数function App() { const clickHandler = (e) => { alert('事件绑定') console.log('事件参数', e) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={clickHandler}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 3. 传递自定义参数语法:绑定事件时改造为箭头函数(通过函数引用的方式实现),通过形参传递function App() { const clickHandler = (name) => { console.log('自定义参数', name) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={() => clickHandler('孙笑川')}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 4. 同时传递事件对象和自定义参数语法:在绑定事件的位置传递事件实参 e,clickHandler 中声明形参,且需要注意参数的顺序function App() { const clickHandler = (name, e) => { console.log('自定义参数', name, '事件参数', e) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={(e) => clickHandler('孙笑川', e)}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App
React - 事件绑定 1. 基础事件绑定语法:on + 事件名称 = { 事件处理方法/函数 }function App() { const clickHandler = () => { alert('事件绑定') } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={clickHandler}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 2. 使用事件对象参数function App() { const clickHandler = (e) => { alert('事件绑定') console.log('事件参数', e) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={clickHandler}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 3. 传递自定义参数语法:绑定事件时改造为箭头函数(通过函数引用的方式实现),通过形参传递function App() { const clickHandler = (name) => { console.log('自定义参数', name) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={() => clickHandler('孙笑川')}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App 4. 同时传递事件对象和自定义参数语法:在绑定事件的位置传递事件实参 e,clickHandler 中声明形参,且需要注意参数的顺序function App() { const clickHandler = (name, e) => { console.log('自定义参数', name, '事件参数', e) } return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={(e) => clickHandler('孙笑川', e)}>Click</button> </div> ) } export default App -
 React - 简介、JSX基础 一、搭建开发环境官网快速开始文档 - 创建一个 React 项目:https://18.react.dev/learn/creating-a-react-appnpx create-react-app react-demo npm start二、JSX 基础1. 概念JSX(JS的语法扩展)是JavaScript 和 XML(HTML)的缩写,表示在 js 代码中编写 HTML 模板结构,它是 React 中编写 UI 模板的方式2. 使用 js 表达式在 JSX 中可以通过大括号语法 {} 识别 js 中的表达式,如:变量、函数调用、方法调用等使用引号传递字符串使用 js 变量函数调用和方法调用使用 js 对象const index = 1 function getName() { return '孙笑川' } function App() { return ( <div className="App"> 这是 React Demo {/* 使用引号传递字符串 */} {'这是 React Demo'} {/* 使用 js 变量 */} {index} {/* 函数调用 */} {getName()} {/* 方法调用 */} {new Date().getDate()} {/* 使用js对象 */} <div style={{ color: 'red' }}>这是 React Demo</div> </div> ); } export default App; 3. 列表渲染const list = [ {id: '1', name: '孙笑川'}, {id: '2', name: '药水哥'}, {id: '3', name: '刘波'} ] function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 渲染列表 */} <ul> {list.map(item => <li key={item.id}>{item.name}</li>)} </ul> </div> ); } export default App; 4. 条件渲染通过逻辑运算符、三元表达式实现基础的条件渲染const flag = true function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 逻辑运算 */} {flag && <span>这是 span 标签</span>} {/* 三元运算 */} {!flag ? <span>这是 span 标签</span> : <p>这是 p 标签</p>} </div> ); } export default App; 5. 复杂条件渲染通过自定义函数 + if 判断语句实现const type = 1 // 0 1 2 function getType() { if (type === 0) { return <div>孙笑川</div> } if (type === 1) { return <div>药水哥</div> } if (type === 2) { return <div>刘波</div> } } function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 复杂条件渲染 */} {getType()} </div> ); } export default App;
React - 简介、JSX基础 一、搭建开发环境官网快速开始文档 - 创建一个 React 项目:https://18.react.dev/learn/creating-a-react-appnpx create-react-app react-demo npm start二、JSX 基础1. 概念JSX(JS的语法扩展)是JavaScript 和 XML(HTML)的缩写,表示在 js 代码中编写 HTML 模板结构,它是 React 中编写 UI 模板的方式2. 使用 js 表达式在 JSX 中可以通过大括号语法 {} 识别 js 中的表达式,如:变量、函数调用、方法调用等使用引号传递字符串使用 js 变量函数调用和方法调用使用 js 对象const index = 1 function getName() { return '孙笑川' } function App() { return ( <div className="App"> 这是 React Demo {/* 使用引号传递字符串 */} {'这是 React Demo'} {/* 使用 js 变量 */} {index} {/* 函数调用 */} {getName()} {/* 方法调用 */} {new Date().getDate()} {/* 使用js对象 */} <div style={{ color: 'red' }}>这是 React Demo</div> </div> ); } export default App; 3. 列表渲染const list = [ {id: '1', name: '孙笑川'}, {id: '2', name: '药水哥'}, {id: '3', name: '刘波'} ] function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 渲染列表 */} <ul> {list.map(item => <li key={item.id}>{item.name}</li>)} </ul> </div> ); } export default App; 4. 条件渲染通过逻辑运算符、三元表达式实现基础的条件渲染const flag = true function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 逻辑运算 */} {flag && <span>这是 span 标签</span>} {/* 三元运算 */} {!flag ? <span>这是 span 标签</span> : <p>这是 p 标签</p>} </div> ); } export default App; 5. 复杂条件渲染通过自定义函数 + if 判断语句实现const type = 1 // 0 1 2 function getType() { if (type === 0) { return <div>孙笑川</div> } if (type === 1) { return <div>药水哥</div> } if (type === 2) { return <div>刘波</div> } } function App() { return ( <div className="App"> {/* 复杂条件渲染 */} {getType()} </div> ); } export default App; -
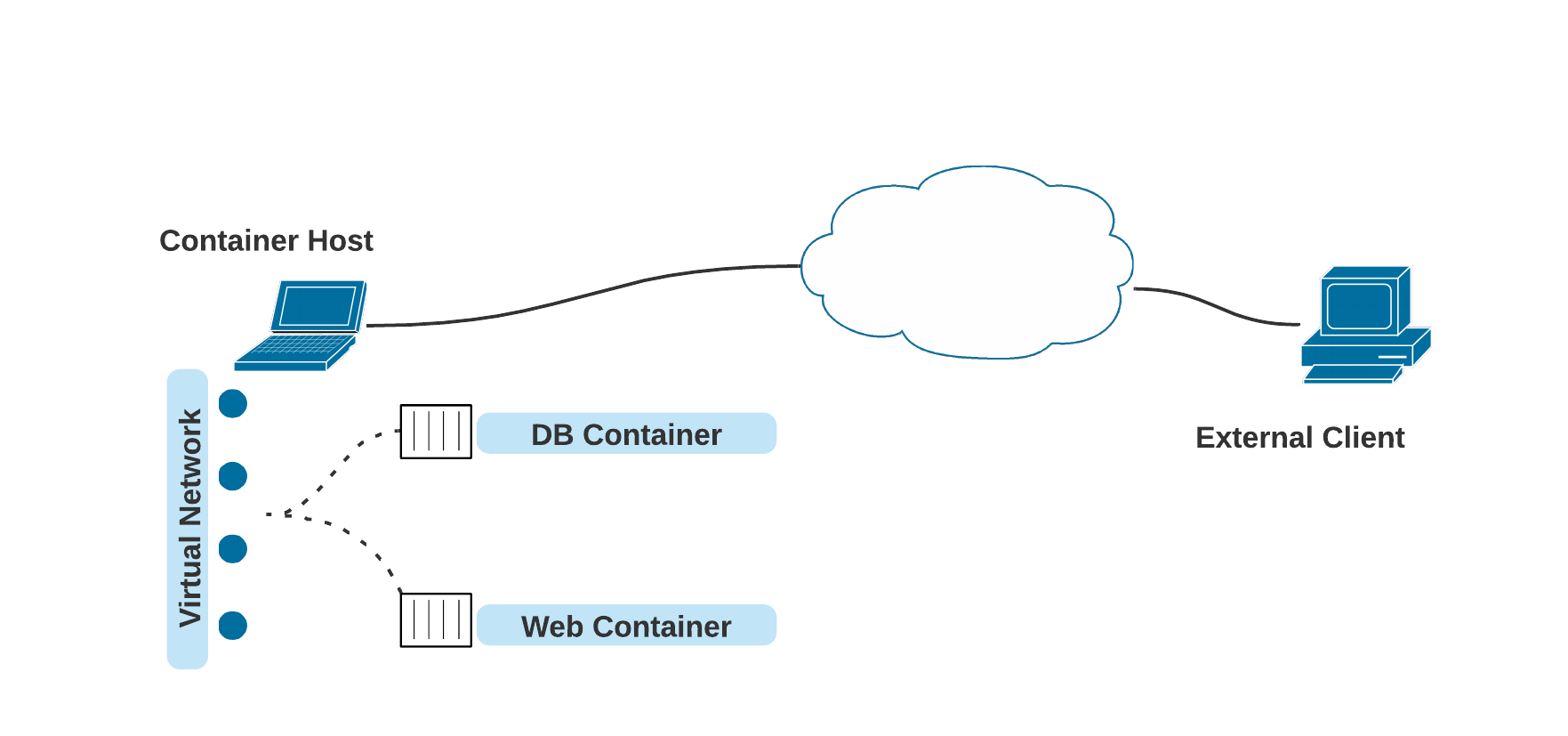
 四、Podman - 网络 1. 简介Podman 管理的容器在进行网络连接时,非特权用户无法在主机上创建网络接口,默认是 slirp4netns,相比于特权用户而言缺少一部分功能,如:无法为容器分配 IP 地址;特权用户运行的容器默认网络模式是 netavark。防火墙当容器执行端口映射时,防火墙也会同步打开对应的端口,但当重新加载防火墙规则时,会删除 netavark iptables,导致容器丢失网络连接,Podman v3 提供了 podman network reload 命令来恢复对应设置,且无需重启容器。2. 桥接桥接指创建一个内部网络,容器和主机都连接到该网络,以此实现容器与外部主机通信Podman 默认使用桥接模式,同时也提供了一个默认的桥接网络,从 4.0 版本开始,非特权用户运行的容器也可以使用 netavark(但不提供默认配置)从旧版本 CNI 切换到 netavark 时,需执行 podman system reset --force 命令,该命令会删除所有的镜像、容器和自定义网络rootless 容器的网络操作是在一个额外的命名空间内执行的,可以通过 podman unshare --rootless-netns 命令加入3. 默认Netavark 是纯内存网络,由于需要向后兼容 Docker,因此不支持 DNS 解析,可通过以下命令修改对应的配置文件# 特权 podman network inspect podman | jq .[] > /etc/containers/networks/podman.json # 非特权 podman network inspect podman | jq .[] > ~/.local/share/containers/storage/networks/podman.json以特权和非特权为例,将服务暴露至主机外# 特权 sudo podman run -d --name webserver -p 8080:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 00f3440c7576aae2d5b193c40513c29c7964e96bf797cf0cc352c2b68ccbe66a # 非特权 podman run -d --name webserver --network podman1 -p 8081:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 269fd0d6b2c8ed60f2ca41d7beceec2471d72fb9a33aa8ca45b81dc9a0abbb12外部客户端可通过8080 或 8081 端口访问到对应的服务4. MacvlanPodman 必须以 root 身份才能操作 macvlan# 创建 macvlan,eth0 为主机的网络接口(与 Docker 的创建方式一致) sudo podman network create -d macvlan -o parent=eth0 macvlan_test macvlan_test # --subnet指定子网,不使用 DHCP(可选) sudo podman network create -d macvlan \ --subnet 192.168.123.0/24 \ --gateway 192.168.123.1 \ -o parent=eth0 \ macvlan_test # 使用 DHCP # 查看当前使用的网络后端 sudo podman info --format {{.Host.NetworkBackend}} # NetAvark 启用 DHCP(以systemd为例) sudo systemctl enable --now netavark-dhcp-proxy.socket # CNI 启用 DHCP(以systemd为例) sudo systemctl enable --now cni-dhcp.socket# 容器使用 macvlan sudo podman run -d --name webserver --network macvlan_test quay.io/libpod/banner 03d82083c434d7e937fc0b87c25401f46ab5050007df403bf988e25e52c5cc40 # 使用外部客户端访问 (outside_host): $ curl http://<容器分配到的ip> ___ __ / _ \___ ___/ /_ _ ___ ____ / ___/ _ \/ _ / ' \/ _ `/ _ \ /_/ \___/\_,_/_/_/_/\_,_/_//_/5. Slirp4netnsSlirp4netns 是 rootless 容器和 Pod 的默认网络配置,它的出现是因为非特权用户无法在主机上创建网络接口。Slirp4netns 会在容器的网络命名空间中创建一个 TAP 设备,并连接到用户模式 TCP/IP 协议栈非特权用户必须使用 1024 到 65535 端口,因为更低的端口需要 root 权限,可以使用以下方法调整默认的设置 sysctl net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_startslirp4netns 网络模式下,容器与容器之间完全隔离,且没有虚拟网络,容器之间要进行通信时,需要使用与宿主机的端口映射,或者将它们放入同一个 Pod 中(即共享同一个网络命名空间)以两个 rootless 容器通信为例# 假设主机 ip 为 192.168.123.123 # 运行 rootless 容器 podman run -d --name webserver -p 8080:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 17ea33ccd7f55ff45766b3ec596b990a5f2ba66eb9159cb89748a85dc3cebfe0 # 运行另一个 rootless 容器,并执行 curl podman run -it quay.io/libpod/banner curl http://192.168.123.123:8080 # 外部客户端访问 (outside_host): $ curl http://192.168.123.123:8080 ___ __ / _ \___ ___/ /_ _ ___ ____ / ___/ _ \/ _ / ' \/ _ `/ _ \ /_/ \___/\_,_/_/_/_/\_,_/_//_/6. 容器与 Pod 之间的通信Podman Pod 中的所有容器共享同一个网络命名空间(即它们将具有相同的 IP 地址、MAC 地址和端口映射),Pod 中的容器之间可以使用 localhost 方便地进行通信如上图所示,该 Pod 中的 DB Container 和 Web Container 所属同一个网络命名空间下,他们之间可以通过 localhost:[port] 进行通信,也可以通过分配给 Pod 的 ip 进行寻址,在 DNS 服务可用时,也可以使用 dns name 进行通信(类似于 K8s 中的 Core DNS)。
四、Podman - 网络 1. 简介Podman 管理的容器在进行网络连接时,非特权用户无法在主机上创建网络接口,默认是 slirp4netns,相比于特权用户而言缺少一部分功能,如:无法为容器分配 IP 地址;特权用户运行的容器默认网络模式是 netavark。防火墙当容器执行端口映射时,防火墙也会同步打开对应的端口,但当重新加载防火墙规则时,会删除 netavark iptables,导致容器丢失网络连接,Podman v3 提供了 podman network reload 命令来恢复对应设置,且无需重启容器。2. 桥接桥接指创建一个内部网络,容器和主机都连接到该网络,以此实现容器与外部主机通信Podman 默认使用桥接模式,同时也提供了一个默认的桥接网络,从 4.0 版本开始,非特权用户运行的容器也可以使用 netavark(但不提供默认配置)从旧版本 CNI 切换到 netavark 时,需执行 podman system reset --force 命令,该命令会删除所有的镜像、容器和自定义网络rootless 容器的网络操作是在一个额外的命名空间内执行的,可以通过 podman unshare --rootless-netns 命令加入3. 默认Netavark 是纯内存网络,由于需要向后兼容 Docker,因此不支持 DNS 解析,可通过以下命令修改对应的配置文件# 特权 podman network inspect podman | jq .[] > /etc/containers/networks/podman.json # 非特权 podman network inspect podman | jq .[] > ~/.local/share/containers/storage/networks/podman.json以特权和非特权为例,将服务暴露至主机外# 特权 sudo podman run -d --name webserver -p 8080:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 00f3440c7576aae2d5b193c40513c29c7964e96bf797cf0cc352c2b68ccbe66a # 非特权 podman run -d --name webserver --network podman1 -p 8081:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 269fd0d6b2c8ed60f2ca41d7beceec2471d72fb9a33aa8ca45b81dc9a0abbb12外部客户端可通过8080 或 8081 端口访问到对应的服务4. MacvlanPodman 必须以 root 身份才能操作 macvlan# 创建 macvlan,eth0 为主机的网络接口(与 Docker 的创建方式一致) sudo podman network create -d macvlan -o parent=eth0 macvlan_test macvlan_test # --subnet指定子网,不使用 DHCP(可选) sudo podman network create -d macvlan \ --subnet 192.168.123.0/24 \ --gateway 192.168.123.1 \ -o parent=eth0 \ macvlan_test # 使用 DHCP # 查看当前使用的网络后端 sudo podman info --format {{.Host.NetworkBackend}} # NetAvark 启用 DHCP(以systemd为例) sudo systemctl enable --now netavark-dhcp-proxy.socket # CNI 启用 DHCP(以systemd为例) sudo systemctl enable --now cni-dhcp.socket# 容器使用 macvlan sudo podman run -d --name webserver --network macvlan_test quay.io/libpod/banner 03d82083c434d7e937fc0b87c25401f46ab5050007df403bf988e25e52c5cc40 # 使用外部客户端访问 (outside_host): $ curl http://<容器分配到的ip> ___ __ / _ \___ ___/ /_ _ ___ ____ / ___/ _ \/ _ / ' \/ _ `/ _ \ /_/ \___/\_,_/_/_/_/\_,_/_//_/5. Slirp4netnsSlirp4netns 是 rootless 容器和 Pod 的默认网络配置,它的出现是因为非特权用户无法在主机上创建网络接口。Slirp4netns 会在容器的网络命名空间中创建一个 TAP 设备,并连接到用户模式 TCP/IP 协议栈非特权用户必须使用 1024 到 65535 端口,因为更低的端口需要 root 权限,可以使用以下方法调整默认的设置 sysctl net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_startslirp4netns 网络模式下,容器与容器之间完全隔离,且没有虚拟网络,容器之间要进行通信时,需要使用与宿主机的端口映射,或者将它们放入同一个 Pod 中(即共享同一个网络命名空间)以两个 rootless 容器通信为例# 假设主机 ip 为 192.168.123.123 # 运行 rootless 容器 podman run -d --name webserver -p 8080:80 quay.io/libpod/banner 17ea33ccd7f55ff45766b3ec596b990a5f2ba66eb9159cb89748a85dc3cebfe0 # 运行另一个 rootless 容器,并执行 curl podman run -it quay.io/libpod/banner curl http://192.168.123.123:8080 # 外部客户端访问 (outside_host): $ curl http://192.168.123.123:8080 ___ __ / _ \___ ___/ /_ _ ___ ____ / ___/ _ \/ _ / ' \/ _ `/ _ \ /_/ \___/\_,_/_/_/_/\_,_/_//_/6. 容器与 Pod 之间的通信Podman Pod 中的所有容器共享同一个网络命名空间(即它们将具有相同的 IP 地址、MAC 地址和端口映射),Pod 中的容器之间可以使用 localhost 方便地进行通信如上图所示,该 Pod 中的 DB Container 和 Web Container 所属同一个网络命名空间下,他们之间可以通过 localhost:[port] 进行通信,也可以通过分配给 Pod 的 ip 进行寻址,在 DNS 服务可用时,也可以使用 dns name 进行通信(类似于 K8s 中的 Core DNS)。 -
 三、Podman - 对镜像进行签名和分发 以 GNU Privacy Guard(GPG)密钥为例如果使用 Podman 在将镜像推送到镜像仓库前对其进行了签名,则拉取时的客户端必须配置为从远程服务器获取签名,未签名的镜像都将被拒绝1. 生成 GPG密钥gpg --full-gen-key # 验证密钥 gpg --list-keys xxx@gmail.com2. 拉取镜像# 拉取镜像 podman pull docker://docker.io/alpine:latest # 查看 podman images alpine REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE docker.io/library/alpine latest e7b39c54cdec 4 weeks ago 8.74 MB # 自定义 tag(localhost:5000 为本地镜像仓库) sudo podman tag alpine localhost:5000/alpine3. 修改配置/etc/containers/registries.d/default.yaml default-docker: sigstore: http://localhost:8000 # 引用网络服务器进行签名读取 sigstore-staging: file:///var/lib/containers/sigstore # 引用文件路径进行签名写入4. 签名并推送镜像sudo -E GNUPGHOME=$HOME/.gnupg \ podman push \ --tls-verify=false \ --sign-by sgrunert@suse.com \ localhost:5000/alpine … Storing signatures推送镜像后,可以看到产生的新的可用签名ls /var/lib/containers/sigstore 'alpine@sha256=e9b65ef660a3ff91d28cc50eba84f21798a6c5c39b4dd165047db49e84ae1fb9'5. 自定义本地8000端口服务bash -c 'cd /var/lib/containers/sigstore && python3 -m http.server' Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...6. 强制签名要求配置nano /etc/containers/policy.json { "default": [{ "type": "insecureAcceptAnything" }], "transports": { "docker": { "localhost:5000": [ { "type": "signedBy", "keyType": "GPGKeys", "keyPath": "/tmp/key.gpg" } ] } } }# 将 GPG 密钥放置到 keyPath 目录下 gpg --output /tmp/key.gpg --armor --export xxx@gmail.com7. 拉取测试# 先删除本地已经拉取的 alpine 镜像 podman rmi docker.io/alpine localhost:5000/alpine # 重新拉取 podman pull --tls-verify=false localhost:5000/alpine此时在8000端口的服务日志中可以看到访问签名的日志8. 错误配置示例keyPath 路径配置错误,在拉取镜像时会报错sudo podman pull --tls-verify=false localhost:5000/alpine Trying to pull localhost:5000/alpine... Error: pulling image "localhost:5000/alpine": unable to pull localhost:5000/alpine: unable to pull image: Source image rejected: Invalid GPG signature: ......
三、Podman - 对镜像进行签名和分发 以 GNU Privacy Guard(GPG)密钥为例如果使用 Podman 在将镜像推送到镜像仓库前对其进行了签名,则拉取时的客户端必须配置为从远程服务器获取签名,未签名的镜像都将被拒绝1. 生成 GPG密钥gpg --full-gen-key # 验证密钥 gpg --list-keys xxx@gmail.com2. 拉取镜像# 拉取镜像 podman pull docker://docker.io/alpine:latest # 查看 podman images alpine REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE docker.io/library/alpine latest e7b39c54cdec 4 weeks ago 8.74 MB # 自定义 tag(localhost:5000 为本地镜像仓库) sudo podman tag alpine localhost:5000/alpine3. 修改配置/etc/containers/registries.d/default.yaml default-docker: sigstore: http://localhost:8000 # 引用网络服务器进行签名读取 sigstore-staging: file:///var/lib/containers/sigstore # 引用文件路径进行签名写入4. 签名并推送镜像sudo -E GNUPGHOME=$HOME/.gnupg \ podman push \ --tls-verify=false \ --sign-by sgrunert@suse.com \ localhost:5000/alpine … Storing signatures推送镜像后,可以看到产生的新的可用签名ls /var/lib/containers/sigstore 'alpine@sha256=e9b65ef660a3ff91d28cc50eba84f21798a6c5c39b4dd165047db49e84ae1fb9'5. 自定义本地8000端口服务bash -c 'cd /var/lib/containers/sigstore && python3 -m http.server' Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...6. 强制签名要求配置nano /etc/containers/policy.json { "default": [{ "type": "insecureAcceptAnything" }], "transports": { "docker": { "localhost:5000": [ { "type": "signedBy", "keyType": "GPGKeys", "keyPath": "/tmp/key.gpg" } ] } } }# 将 GPG 密钥放置到 keyPath 目录下 gpg --output /tmp/key.gpg --armor --export xxx@gmail.com7. 拉取测试# 先删除本地已经拉取的 alpine 镜像 podman rmi docker.io/alpine localhost:5000/alpine # 重新拉取 podman pull --tls-verify=false localhost:5000/alpine此时在8000端口的服务日志中可以看到访问签名的日志8. 错误配置示例keyPath 路径配置错误,在拉取镜像时会报错sudo podman pull --tls-verify=false localhost:5000/alpine Trying to pull localhost:5000/alpine... Error: pulling image "localhost:5000/alpine": unable to pull localhost:5000/alpine: unable to pull image: Source image rejected: Invalid GPG signature: ...... -
 二、Podman - 安装和基础命令 1. 安装以 Debian 12 为例apt install podman root@debian:~# podman version Client: Podman Engine Version: 4.3.1 API Version: 4.3.1 Go Version: go1.19.8 Built: Thu Jan 1 08:00:00 1970 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 2. 基础命令运行示例容器# 以基础的 httpd 服务为例 podman run --name nginx-test -d -p 8080:80/tcp docker.io/nginx注:该命令下容器以分离模式运行(-d),Podman 会在运行结束后打印容器ID列出正在运行的容器podman ps # 列出所有容器 podman ps -a检查运行中的容器podman inspect <container>注:由于容器以 rootless 模式运行,因此不会分配 IP 地址,inspect 信息中该项的值为 none测试 httpd 服务root@debian:~# curl http://localhost:8080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html> 查看容器日志podman logs -f <container_id>root@debian:~# podman logs nginx-test /docker-entrypoint.sh: /docker-entrypoint.d/ is not empty, will attempt to perform configuration /docker-entrypoint.sh: Looking for shell scripts in /docker-entrypoint.d/ /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh 10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh: info: Getting the checksum of /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf 10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh: info: Enabled listen on IPv6 in /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf /docker-entrypoint.sh: Sourcing /docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/20-envsubst-on-templates.sh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/30-tune-worker-processes.sh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Configuration complete; ready for start up 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: using the "epoll" event method 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: nginx/1.29.4 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: built by gcc 14.2.0 (Debian 14.2.0-19) 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: OS: Linux 6.1.0-41-amd64 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE): 1048576:1048576 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker processes 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 24 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 25 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 26 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 27 10.88.0.1 - - [14/Jan/2026:14:05:38 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 615 "-" "curl/7.88.1" "-" 查看容器信息和进程root@debian:~# podman top nginx-test USER PID PPID %CPU ELAPSED TTY TIME COMMAND root 1 0 0.000 2m26.588290297s ? 0s nginx: master process nginx -g daemon off; nginx 24 1 0.000 2m26.588345391s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 25 1 0.000 2m26.588369296s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 26 1 0.000 2m26.588388167s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 27 1 0.000 2m26.588406535s ? 0s nginx: worker process 检查容器对容器进行检查点操作会停止容器运行,并将容器内所有进程的状态写入磁盘,在有需要的时候可以恢复,并从检查点创建时的状态继续运行(此功能需要系统上安装 CRIU 3.11 或更高版本,且不支持 rootless)sudo podman container checkpoint <container_id>恢复容器创建过检查点的容器才支持快照sudo podman container restore <container_id>迁移容器创建检查点 ---> 将对应文件传输至目标主机 ---> 目标主机恢复容器# 原主机 sudo podman container checkpoint <container_id> -e /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz scp /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz <destination_host>:/tmp # 目标主机 sudo podman container restore -i /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz 停止容器podman stop <container_id>移除容器podman rm <container_id>
二、Podman - 安装和基础命令 1. 安装以 Debian 12 为例apt install podman root@debian:~# podman version Client: Podman Engine Version: 4.3.1 API Version: 4.3.1 Go Version: go1.19.8 Built: Thu Jan 1 08:00:00 1970 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 2. 基础命令运行示例容器# 以基础的 httpd 服务为例 podman run --name nginx-test -d -p 8080:80/tcp docker.io/nginx注:该命令下容器以分离模式运行(-d),Podman 会在运行结束后打印容器ID列出正在运行的容器podman ps # 列出所有容器 podman ps -a检查运行中的容器podman inspect <container>注:由于容器以 rootless 模式运行,因此不会分配 IP 地址,inspect 信息中该项的值为 none测试 httpd 服务root@debian:~# curl http://localhost:8080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html> 查看容器日志podman logs -f <container_id>root@debian:~# podman logs nginx-test /docker-entrypoint.sh: /docker-entrypoint.d/ is not empty, will attempt to perform configuration /docker-entrypoint.sh: Looking for shell scripts in /docker-entrypoint.d/ /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh 10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh: info: Getting the checksum of /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf 10-listen-on-ipv6-by-default.sh: info: Enabled listen on IPv6 in /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf /docker-entrypoint.sh: Sourcing /docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/20-envsubst-on-templates.sh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Launching /docker-entrypoint.d/30-tune-worker-processes.sh /docker-entrypoint.sh: Configuration complete; ready for start up 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: using the "epoll" event method 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: nginx/1.29.4 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: built by gcc 14.2.0 (Debian 14.2.0-19) 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: OS: Linux 6.1.0-41-amd64 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: getrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE): 1048576:1048576 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker processes 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 24 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 25 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 26 2026/01/14 14:05:20 [notice] 1#1: start worker process 27 10.88.0.1 - - [14/Jan/2026:14:05:38 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 615 "-" "curl/7.88.1" "-" 查看容器信息和进程root@debian:~# podman top nginx-test USER PID PPID %CPU ELAPSED TTY TIME COMMAND root 1 0 0.000 2m26.588290297s ? 0s nginx: master process nginx -g daemon off; nginx 24 1 0.000 2m26.588345391s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 25 1 0.000 2m26.588369296s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 26 1 0.000 2m26.588388167s ? 0s nginx: worker process nginx 27 1 0.000 2m26.588406535s ? 0s nginx: worker process 检查容器对容器进行检查点操作会停止容器运行,并将容器内所有进程的状态写入磁盘,在有需要的时候可以恢复,并从检查点创建时的状态继续运行(此功能需要系统上安装 CRIU 3.11 或更高版本,且不支持 rootless)sudo podman container checkpoint <container_id>恢复容器创建过检查点的容器才支持快照sudo podman container restore <container_id>迁移容器创建检查点 ---> 将对应文件传输至目标主机 ---> 目标主机恢复容器# 原主机 sudo podman container checkpoint <container_id> -e /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz scp /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz <destination_host>:/tmp # 目标主机 sudo podman container restore -i /tmp/checkpoint.tar.gz 停止容器podman stop <container_id>移除容器podman rm <container_id> -
 一、Podman - 简介 一、简介1. 概念Podman 是一个无守护进程、开源、Linux原生的工具,遵循 OCI 开放容器倡议的容器合容器镜像,可以轻松的查找、运行、构建、共享和部署应用程序。与其他常见的容器(Docker、CRI-O、Containerd)类似,Podman 依赖于一个符合 OCI 规范的容器运行时(如 runc、crun、runv 等)来与操作系统交互并创建运行中的容器。2. 特性Podman 容器支持 root / rootless 模式,其使用 libpod 库来管理整个容器生态系统,包括 Pod、容器、容器镜像和容器卷。Linux 环境下提供管理容器的 RESTful API
一、Podman - 简介 一、简介1. 概念Podman 是一个无守护进程、开源、Linux原生的工具,遵循 OCI 开放容器倡议的容器合容器镜像,可以轻松的查找、运行、构建、共享和部署应用程序。与其他常见的容器(Docker、CRI-O、Containerd)类似,Podman 依赖于一个符合 OCI 规范的容器运行时(如 runc、crun、runv 等)来与操作系统交互并创建运行中的容器。2. 特性Podman 容器支持 root / rootless 模式,其使用 libpod 库来管理整个容器生态系统,包括 Pod、容器、容器镜像和容器卷。Linux 环境下提供管理容器的 RESTful API -
 五、DestinationRule 1. 概念字段名称说明spec.host关联 DestinationRule 配置的服务名称,可以是自动发现的服务(例如Kubernetes service name),或通过 ServiceEntry 声明的 hosts。如填写的服务名无法在上述源中找到。则该 DestinationRule 中定义的规则无效spec.subsets定义服务的版本(subsets),版本可通过标签键值对匹配服务中的endpoints。可以在 subsets 级覆盖流量策略配置spec.trafficPolicy定义流量策略,包括负载均衡、连接池、健康检查、TLS 策略等spec.spec.trafficPolicy.loadBalancer配置负载均衡算法,可配置:简单负载均衡算法(round robin,least conn,random...) ,一致性哈希(会话保持,支持按 header name,cookie,IP,query parameter 哈希),地域感知负载均衡算法spec.trafficPolicy.connectionPool配置与上游服务的连接量,可设置 TCP/HTTP 连接池spec.trafficPolicy.outlierDetection配置从负载均衡池中驱逐不健康的 hostsspec.trafficPolicy.tls连接上游服务的 client 端 TLS 相关配置,与 PeerAuthentication 策略(server 端 TLS 模式配置)配合使用spec.trafficPolicy.portLevelSettings配置端口级的流量策略,该策略会覆盖服务 / subsets 级别的流量策略配置DestinationRule 在路由发生后应用于流量,支持如下配置:负载均衡连接池局部异常点检测客户端 TLS 配置端口流量策略2. 负载均衡设置通过负载均衡设置,可以控制目的地使用的负载均衡算法apiVersion: netweorking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: DestinationRule metadata: name: nginx-destination spec: host: nginx.test.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: loadBalancer: simple: ROUND_ROBIN # 轮询 subsets: - name: v1 labels: version: vl - name: v2 labels: version: v2simple字段:ROUND_ROBIN:轮询算法,如果未指定则默认采用这种算法LEAST_CONN:最少连接算法,从两个随机选择的服务选择一个活动请求数较少的后端实例RANDOM:从可用的健康实例中随机选择一个PASSTHROUGH:直接转发连接到客户端连接的目标地址,即不做做负载均衡consistentHash 字段:httpHeaderName:基于 HeaderhttpCookie:基于 CookieuseSourcelp:基于源 IP 计算哈希值minimumRingSize:哈希环上虚拟节点数的最小值,节点数越多则负载均衡越精细trafficPolicy: loadBalancer: consistentHash: httpCokkie: name: location ttl: 2s3. 连接池配置可以在 TCP 和 HTTP 层面应用于上游服务的每个主机,可以用它们来控制连接量tcp 连接池配置:maxConnections:上游服务的所有实例建立的最大连接数,默认值1024,属于 TCP 层的配置,对于HTTP,只作用于 HTTP/1.1,因为 HTTP/2 对每个主机都使用单个连接connectTimeout:TCP 连接超时,表示主机网络连接超时,可以改善因调用服务变慢而导致整个链路变慢的情况tcpKeepalive:lstio1.1 版本开始新支持的配置,定期给对端发送一个 keepalive 探测包,判断连接是否可用spec: host: nginx.test.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 50 connectTimeout: 25ms tcpKeepalive: probes: 5 time: 3600 interval: 60shttp 连接池配置:http1MaxPendingRequests:最大等待 HTTP 请求数,默认值1024,只适用于 HTTP/1.1 的服务,因为 HTTP/2 协议的请求在到来时会立即复用连接,不会在连接池等待http2MaxRequests:最大请求数,默认值1024,只适用于 HTTP/2 服务,因为 HTTP/1.1 使用最大连接数 maxConnections 即可,表示上游服务的所有实例处理的最大请求数maxRequestsPerConnection:每个连接的最大请求数,HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 连接池都遵循此参数,如果没有设置,则代表不限制设置为1时表示每个连接只处理一个请求,相当于禁用了 Keep-alivemaxRetries:最大重试次数,默认值3,表示服务可以执行的最大重试次数。如果调用端因为偶发的抖动导致请求直接失败,则可能会带来业务损失,一般建议配置重试,若重试成功则可正常返回数据,只不过比原来响应得慢一点,但如果重试次数太多,会对性能造成一定的影响idleTimeout:空闲超时,即:在多长时间内没有活动请求则关闭连接# 配置最大80个连接,最多100个并发请求,每个请求的连接数不超过10个,超时时间为30ms spec: host: nginx.test.cluster.local trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 80 connectTimeout: 30ms http: http2MaxRequests: 100 maxRequestsPerConnection: 104. 异常点检测异常点检测是一个断路器的实现,它跟踪上游服务中每个主机(Pod)的状态,如果其中一个主机开始返回 5xx HTTP 错误,它就会在预定的时间内被从负载均衡池中弹出,对于 TCP 服务,Envoy 将连接超时或失败计算为错误。两种健康检查:主动检查:定期探测目标服务实例,根据应答来判断服务实例的健康状态,如负载均衡器中的健康检查被动检查:通过实际的访问情况来找出不健康的实例,如 Istio 中的异常点检查异常实例检查相关的配置:consecutiveErrors:实例被驱逐前的连续错误次数,默认值5。对于 HTTP 服务,返回502、503 和 504 的请求会被认为异常;对于 TCP 服务,连接超时或者连接错误事件会被认为异常interval:驱逐的时间间隔,默认值10秒,要求大于1毫秒,单位可以是时、分、毫秒baseEjectionTime:最小驱逐时间,一个实例被驱逐的时间等于这个最小驱逐时间乘以驱逐的次数,这样一个因多次异常被驱逐的实例,被驱逐的时间会越来越长,默认值30秒,要求大于1毫秒,单位可以是时、分、毫秒maxEjectionPercent:指负载均衡池中可以被驱逐的故障实例的最大比例,默认值10%,该设置是为了避免太多的服务实例被驱逐导致服务整体能力下降minHealthPercent:最小健康实例比例,是 lstio 1.1 新增的配置,当负载均衡池中的健康实例数的比例大于这个比例时,异常点检查机制可用,反之该功能将被禁用;所有服务实例不管被认定为健康还是不健康,都可以接收请求,参数的默认值为50%# 最大500个http2请求,每个连接不超过10个请求,每5分钟扫描一次上游主机(Pod),如果其中任何一个主机连续失败10次,Envoy 会将其弹出10分钟 trafficPolicy: coninectionPool: http: http2MaxRequests: 500 maxRequestsPerConnection: 10 outlierDetection: consecutiveErrors: 10 interval: 5m baseEjectionTime: 1om5. TLS 设置其包含任何与上游服务连接的 TLS 相关设置trafficPolicy: tls: mode: MUTUAL clientCertificate: ./certs/cert.pem privatekey: ./certs/key - pem caCertificates: ./certs/ca.pemmTLS:双向认证,客户端和服务端都通过证书颁发机构验证彼此的身份,即:由同一个 root ca 生成两套证书,客户端、服务端各一个,客户端通过 https 访问服务时,双方会交换证书,并进行认证,认证通过后即可进行通信TLS 模式:DISABLE:无 TLS 连接SIMPLE:在上游端点发起 TLS 连接ISTIO_MUTUAL:与 MUTUAL 类似,使用 Istio 的 mTLS 证书6. 端口流量策略在端口上配置流量策略,配置后其会覆盖全局的流量策略trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 80 portLevelSettings: - port: number: 80 loadBalancer: simple: LEAST_CONN connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 100 - port: number: 80 loadBalancer: simple: ROUND_ROBIN7. 服务子集subset:定义服务的子集name:服务子集的名称,必填字段,VirtualService 通过该属性引用label:标签,通过一组标签定义属于这个服务子集的实例,如:version(版本)trafficPolicy:应用到该子集上的流量策略# 给名称为 nginx-v1 的服务子集配置最大连接数 spec: hosts: nginx subsets: - name: nginx-v1 labels: version: v2 trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 100
五、DestinationRule 1. 概念字段名称说明spec.host关联 DestinationRule 配置的服务名称,可以是自动发现的服务(例如Kubernetes service name),或通过 ServiceEntry 声明的 hosts。如填写的服务名无法在上述源中找到。则该 DestinationRule 中定义的规则无效spec.subsets定义服务的版本(subsets),版本可通过标签键值对匹配服务中的endpoints。可以在 subsets 级覆盖流量策略配置spec.trafficPolicy定义流量策略,包括负载均衡、连接池、健康检查、TLS 策略等spec.spec.trafficPolicy.loadBalancer配置负载均衡算法,可配置:简单负载均衡算法(round robin,least conn,random...) ,一致性哈希(会话保持,支持按 header name,cookie,IP,query parameter 哈希),地域感知负载均衡算法spec.trafficPolicy.connectionPool配置与上游服务的连接量,可设置 TCP/HTTP 连接池spec.trafficPolicy.outlierDetection配置从负载均衡池中驱逐不健康的 hostsspec.trafficPolicy.tls连接上游服务的 client 端 TLS 相关配置,与 PeerAuthentication 策略(server 端 TLS 模式配置)配合使用spec.trafficPolicy.portLevelSettings配置端口级的流量策略,该策略会覆盖服务 / subsets 级别的流量策略配置DestinationRule 在路由发生后应用于流量,支持如下配置:负载均衡连接池局部异常点检测客户端 TLS 配置端口流量策略2. 负载均衡设置通过负载均衡设置,可以控制目的地使用的负载均衡算法apiVersion: netweorking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: DestinationRule metadata: name: nginx-destination spec: host: nginx.test.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: loadBalancer: simple: ROUND_ROBIN # 轮询 subsets: - name: v1 labels: version: vl - name: v2 labels: version: v2simple字段:ROUND_ROBIN:轮询算法,如果未指定则默认采用这种算法LEAST_CONN:最少连接算法,从两个随机选择的服务选择一个活动请求数较少的后端实例RANDOM:从可用的健康实例中随机选择一个PASSTHROUGH:直接转发连接到客户端连接的目标地址,即不做做负载均衡consistentHash 字段:httpHeaderName:基于 HeaderhttpCookie:基于 CookieuseSourcelp:基于源 IP 计算哈希值minimumRingSize:哈希环上虚拟节点数的最小值,节点数越多则负载均衡越精细trafficPolicy: loadBalancer: consistentHash: httpCokkie: name: location ttl: 2s3. 连接池配置可以在 TCP 和 HTTP 层面应用于上游服务的每个主机,可以用它们来控制连接量tcp 连接池配置:maxConnections:上游服务的所有实例建立的最大连接数,默认值1024,属于 TCP 层的配置,对于HTTP,只作用于 HTTP/1.1,因为 HTTP/2 对每个主机都使用单个连接connectTimeout:TCP 连接超时,表示主机网络连接超时,可以改善因调用服务变慢而导致整个链路变慢的情况tcpKeepalive:lstio1.1 版本开始新支持的配置,定期给对端发送一个 keepalive 探测包,判断连接是否可用spec: host: nginx.test.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 50 connectTimeout: 25ms tcpKeepalive: probes: 5 time: 3600 interval: 60shttp 连接池配置:http1MaxPendingRequests:最大等待 HTTP 请求数,默认值1024,只适用于 HTTP/1.1 的服务,因为 HTTP/2 协议的请求在到来时会立即复用连接,不会在连接池等待http2MaxRequests:最大请求数,默认值1024,只适用于 HTTP/2 服务,因为 HTTP/1.1 使用最大连接数 maxConnections 即可,表示上游服务的所有实例处理的最大请求数maxRequestsPerConnection:每个连接的最大请求数,HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 连接池都遵循此参数,如果没有设置,则代表不限制设置为1时表示每个连接只处理一个请求,相当于禁用了 Keep-alivemaxRetries:最大重试次数,默认值3,表示服务可以执行的最大重试次数。如果调用端因为偶发的抖动导致请求直接失败,则可能会带来业务损失,一般建议配置重试,若重试成功则可正常返回数据,只不过比原来响应得慢一点,但如果重试次数太多,会对性能造成一定的影响idleTimeout:空闲超时,即:在多长时间内没有活动请求则关闭连接# 配置最大80个连接,最多100个并发请求,每个请求的连接数不超过10个,超时时间为30ms spec: host: nginx.test.cluster.local trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 80 connectTimeout: 30ms http: http2MaxRequests: 100 maxRequestsPerConnection: 104. 异常点检测异常点检测是一个断路器的实现,它跟踪上游服务中每个主机(Pod)的状态,如果其中一个主机开始返回 5xx HTTP 错误,它就会在预定的时间内被从负载均衡池中弹出,对于 TCP 服务,Envoy 将连接超时或失败计算为错误。两种健康检查:主动检查:定期探测目标服务实例,根据应答来判断服务实例的健康状态,如负载均衡器中的健康检查被动检查:通过实际的访问情况来找出不健康的实例,如 Istio 中的异常点检查异常实例检查相关的配置:consecutiveErrors:实例被驱逐前的连续错误次数,默认值5。对于 HTTP 服务,返回502、503 和 504 的请求会被认为异常;对于 TCP 服务,连接超时或者连接错误事件会被认为异常interval:驱逐的时间间隔,默认值10秒,要求大于1毫秒,单位可以是时、分、毫秒baseEjectionTime:最小驱逐时间,一个实例被驱逐的时间等于这个最小驱逐时间乘以驱逐的次数,这样一个因多次异常被驱逐的实例,被驱逐的时间会越来越长,默认值30秒,要求大于1毫秒,单位可以是时、分、毫秒maxEjectionPercent:指负载均衡池中可以被驱逐的故障实例的最大比例,默认值10%,该设置是为了避免太多的服务实例被驱逐导致服务整体能力下降minHealthPercent:最小健康实例比例,是 lstio 1.1 新增的配置,当负载均衡池中的健康实例数的比例大于这个比例时,异常点检查机制可用,反之该功能将被禁用;所有服务实例不管被认定为健康还是不健康,都可以接收请求,参数的默认值为50%# 最大500个http2请求,每个连接不超过10个请求,每5分钟扫描一次上游主机(Pod),如果其中任何一个主机连续失败10次,Envoy 会将其弹出10分钟 trafficPolicy: coninectionPool: http: http2MaxRequests: 500 maxRequestsPerConnection: 10 outlierDetection: consecutiveErrors: 10 interval: 5m baseEjectionTime: 1om5. TLS 设置其包含任何与上游服务连接的 TLS 相关设置trafficPolicy: tls: mode: MUTUAL clientCertificate: ./certs/cert.pem privatekey: ./certs/key - pem caCertificates: ./certs/ca.pemmTLS:双向认证,客户端和服务端都通过证书颁发机构验证彼此的身份,即:由同一个 root ca 生成两套证书,客户端、服务端各一个,客户端通过 https 访问服务时,双方会交换证书,并进行认证,认证通过后即可进行通信TLS 模式:DISABLE:无 TLS 连接SIMPLE:在上游端点发起 TLS 连接ISTIO_MUTUAL:与 MUTUAL 类似,使用 Istio 的 mTLS 证书6. 端口流量策略在端口上配置流量策略,配置后其会覆盖全局的流量策略trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 80 portLevelSettings: - port: number: 80 loadBalancer: simple: LEAST_CONN connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 100 - port: number: 80 loadBalancer: simple: ROUND_ROBIN7. 服务子集subset:定义服务的子集name:服务子集的名称,必填字段,VirtualService 通过该属性引用label:标签,通过一组标签定义属于这个服务子集的实例,如:version(版本)trafficPolicy:应用到该子集上的流量策略# 给名称为 nginx-v1 的服务子集配置最大连接数 spec: hosts: nginx subsets: - name: nginx-v1 labels: version: v2 trafficPolicy: connectionPool: tcp: maxConnections: 100 -
 五、流量管理 - VirtualService 通过 VirtualService,可以定义流量路由规则字段名说明spec.hosts定义路由规则关联一组的hosts,可以是带有通配符的DNS名称或者IP地址(IP地址仅能应用于来源流量为边缘代理网关)。该字段能应用于 HTTP 和 TCP 流量。在 Kubernetes 环境中,可以使用 service 的名称作为缩写,lstio 会按照 VirtualService 所在 namespace 补齐缩写,例如在 default namespace 的 VirtualService 包含 host 缩写 reviews 会被补齐为 reviews.default.svc.cluster.local,为避免误配置,推荐填写 host 全称。spec.gateway定义应用路由规则的来源流量,可以是一个或多个网关,或网格内部的 sidecar,指定方式为[gateway namespace]/[gateway name],保留字段 mesh 表示网格内部所有的 sidecar,当该参数缺省时,会默认填写 mesh,即该路由规则的来源流量为网格内部所有的 sidecar。spec.http定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于 HTTP 流量的路由规则,HTTP 路由规则会应用于网格内部的 service 端口命名为http-, http2-,grpc- 开头的流量以及来自 gateway 的协议为 HTTP,HTTP2,GRPC,TLS-Terminated-HTTPS 的流量。spec.http.match定义路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.http.route定义路由转发目的地列表,一条 HTTP 路由可以是重定向或转发(默认),转发的目的地可以是一个或多个服务(服务版本),同时也可以配置权重、header 操作等行为。spec.http.redirect定义路由重定向,一条 HTTP 路由可以是重定向或转发(默认),如规则中指定了 passthrough 选项,route.redirect 均会被忽略,可将 HTTP 301重定向到另外的 URL 或Authority。spec.http.rewrite定义重写HTTP URL 或 Authority headers,不能与重定向同时配置,重写操作会在转发前执行。spec.http.timeout请求超时时间spec.http.retries请求重试次数spec.http.fault故障注入策略,开启时超时和重试策略不生效spec.http.mirror定义将 HTTP 流量复制到另一个指定的目的端,被复制的流量按照“best effort”原则,sidecar / 网关不会等待复制流量的响应结果就会从源目的端返回响应。spec.http.mirrorPercent定义镜像流量的复制百分比,默认值为100,即100%spec.http.corsPolicy定义 CORS 策略spec.http.headers定义 header 操作规则,包括 request 和 response header 的增删改。spec.tcp定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于 TCP 流量的路由规则,该规则会应用于任何非 HTTP 和 TLS 的端口。spec.tcp.match定义路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.tcp.route定义 TCP 连接转发的目的端。spec.tls定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于未终止的 TLS 或 HTTPS 流量的路由规则,该路由规则会应用于网格内部的 service 端口命名为 https-,tls- 开头的流量,来自 gateway 的端口协议为 HTTPS,TLS 的未终止加密流量,ServiceEntry 使用 HTTPS,TLS 协议的端口,当 https-,tls- 端口未关联 VirtualService 规则时将会被视为 TCP 流量。spec.tls.match定义 TLS 流量路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.tls.route定义连接转发的目的端2.1 routeHTTP Route 规则的功能:满足 HTTPMatchRequest 条件的流量都会被路由到 HTTPRouteDestination,执行重定向(HTTPRedirect)、重写(HTTPRewrite)、重试(HTTPRetry)、故障注入(HTTPFaultInjection)、跨站(CorsPolicy)等策略。2.2 matchmatch 是路由的匹配规则,支持 uri、scheme、method、authority 等字段,且支持 perfix(前缀)、exact(精确)、regex(正则)三种匹配模式:# 匹配 uri 以 test 开头的请求 - match: - uri: prefix: "/test"# 匹配 header 中 key 为 source,value 为 abc 的请求 - match: - headers: source: exact: abc# 根据来源标签匹配 - match: sourceLabels: app: nginx version: v1# 匹配 header 中 key 为 source,value 为 test1 的请求 或 uri 以 test2 开头的请求 - match: - headers: source: exact: abc uri: prefix: "/test1" - uri: prefix: "/test2"2.3 路由目标(RouteDestionation)在 HTTPRouteDestionation 中主要包含三个字段:destination(请求目标)、weight(权重)、headers(请求头),其中 destination 必填。destination:通过 host、subset 和 port 三个属性描述,表示最终将流量路由到此目标。host 是 Destination 必选字段,表示在 lstio 中注册的服务名(建议写全域名),subset 表示在 host 上定义的一个子集,如:在灰度发布中将版本定义为 subset,配置路由策略会将流量转发到不同版本的 subset 上。spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 destination: host: test.com subset : v2weight:表示流量分配的比例,在一个 route 下多个 destination 的 weight 总和要求是100(默认100,必填字段)。如:从原有的 v1 版本中切分 20% 的流量到 v2 版本,这也是灰度发布常用的一个流量策略,即不区分内容,平等的从总流量中切出一部分流量给新版本。spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 weight: 80 destination: host: test.com subset : v2 weight: 20headers:提供了对 HTTP header 的一种操作机制,可以修改一次 HTTP 请求中的Request 或 Response 的值,包含 request 和 response 两个字段。request:表示在发请求给目标地址时修改 Request 的 headerresponse:表示在返回应答时修改 Response 的 header对应的类型都是 HeaderOperations 类型,使用set、add、remove字段来定义对 Header 的操作set:使用map上的key和value覆盖 Request 和 Response 中对应的 Headeradd:追加map上的key和value到原有的 Headerremove:删除在列表中指定的 Header2.4 HTTP重定向(HTTPRedirect)HTTPRedirect 包含两个字段来表示重定向的目标:uri:替换 URL 中的 uri 部分authority:替换 URL 中的 authority 部分# 对 nginx 服务中,所有前缀为 test1 的请求都会被重定向到 new-test 的 /test/a1 地址 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - match: - uri: prefix: /test1 redirect: uri: /test/a1 authority: new-test.com2.5 HTTP重写(HTTPRewrite)通过 HTTP 重写可以在将请求转发给目标服务前修改 HTTP 请求中指定部分的内容,HTTP 重写对用户是不可见的(在服务端执行)HTTPRewrite 包含两个字段:uri:重写 URL 中的 uri 部分authority:重写 URL 中的 authority 部分和 HTTPRedirect 规则稍有不同的是,HTTPRedirect 的 uri 只能替换全部的 path,但 HTTPRewrite 的 uri 是可以重写前缀的,即匹配条件是前缀匹配,则只修改匹配到的前缀。# 将请求前缀中的 /test1 重写为 /test/a1 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - match: - uri: prefix: /test1 rewrite: uri: /test/a1 route: - destination: host: new-test2.6 HTTP重试(HTTPRetry)HTTPRetry 可以定义请求失败时的重试策略,包含三个字段:attempts:必选字段,定义重试的次数perTryTimeout:每次重试超时的时间,单位可以是 ms、s、m和hretryOn:进行重试的条件,多个条件时以逗号分隔5xx:在上游服务返回 5xx 应答码,或者在没有返回时重试gateway-error:类似于5xx异常,只对502、503和504应答码进行重试connect-failure:在链接上游服务失败时重试retriable-4xx:在上游服务返回可重试的4xx应答码时执行重试refused-stream:在上游服务使用 REFUSED_STREAM 错误码重置时执行重试cancelled:gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 cancelled 时执行重试deadline-exceeded:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 deadline-exceeded 时执行重试internal:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 internal 时执行重试resource-exhausted:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 resource-exhausted 时执行重试unavailable:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 unavailable 时执行重试apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com retries: attempts: 3 perTryTimeout: 5s retryOn: 5xx,connect-failure2.7 HTTP流量镜像(HTTPMirror)HTTP 流量镜像指的是将流量转发到原目标地址的同时将流量给另外一个目标地址镜像一份。把生产环境中的实际流量镜像一份到另外一个系统上,完全不会对生产系统产生影响,这里只是镜像了一份流量,数据面代理只需要关注原来转发的流量就可以,不用等待镜像目标地址的返回。apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 mirror: host: test.net subset: v22.8 HTTP故障注入(HTTPFaultInjection)HTTPFaultInjection 通过 delay 和 abort 设置延时和中止两种故障,分别表示 Proxy 延迟转发和终止 HTTP 请求。delay 包含以下两个字段:fixedDelay:必选,表示延迟时间,单位可以是毫秒,秒,分钟和小时,要求至少要大于1毫秒percentage:延时作用在多少比例的请求上# 让 1.5% 的请求延时 5s apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 fault: delay: fixedDelay: 5s percentage: value: 1.5abort 包含以下两个字段:httpStatus:必选,http 状态码percentage:终止故障作用在多少比例的请求上# 让 1.5% 的请求返回 500 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 fault: abort: httpStatus: 500 percentage: value: 1.52.9 HTTP跨域资源共享(CorsPolicy)在 VirtualService 中可以对满足条件的请求配置跨域资源共享,allowOrigin,allowMethods,allowHeader,exposeHeader,maxAge,allowCredentials,等都被转化为 Access-Control-* 的 Header。# 允许来自 new-test.com 的 GET 请求 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 corsPolicy: allowOrigin: - new-test.com allowMethod: - GET maxAge: 2d
五、流量管理 - VirtualService 通过 VirtualService,可以定义流量路由规则字段名说明spec.hosts定义路由规则关联一组的hosts,可以是带有通配符的DNS名称或者IP地址(IP地址仅能应用于来源流量为边缘代理网关)。该字段能应用于 HTTP 和 TCP 流量。在 Kubernetes 环境中,可以使用 service 的名称作为缩写,lstio 会按照 VirtualService 所在 namespace 补齐缩写,例如在 default namespace 的 VirtualService 包含 host 缩写 reviews 会被补齐为 reviews.default.svc.cluster.local,为避免误配置,推荐填写 host 全称。spec.gateway定义应用路由规则的来源流量,可以是一个或多个网关,或网格内部的 sidecar,指定方式为[gateway namespace]/[gateway name],保留字段 mesh 表示网格内部所有的 sidecar,当该参数缺省时,会默认填写 mesh,即该路由规则的来源流量为网格内部所有的 sidecar。spec.http定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于 HTTP 流量的路由规则,HTTP 路由规则会应用于网格内部的 service 端口命名为http-, http2-,grpc- 开头的流量以及来自 gateway 的协议为 HTTP,HTTP2,GRPC,TLS-Terminated-HTTPS 的流量。spec.http.match定义路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.http.route定义路由转发目的地列表,一条 HTTP 路由可以是重定向或转发(默认),转发的目的地可以是一个或多个服务(服务版本),同时也可以配置权重、header 操作等行为。spec.http.redirect定义路由重定向,一条 HTTP 路由可以是重定向或转发(默认),如规则中指定了 passthrough 选项,route.redirect 均会被忽略,可将 HTTP 301重定向到另外的 URL 或Authority。spec.http.rewrite定义重写HTTP URL 或 Authority headers,不能与重定向同时配置,重写操作会在转发前执行。spec.http.timeout请求超时时间spec.http.retries请求重试次数spec.http.fault故障注入策略,开启时超时和重试策略不生效spec.http.mirror定义将 HTTP 流量复制到另一个指定的目的端,被复制的流量按照“best effort”原则,sidecar / 网关不会等待复制流量的响应结果就会从源目的端返回响应。spec.http.mirrorPercent定义镜像流量的复制百分比,默认值为100,即100%spec.http.corsPolicy定义 CORS 策略spec.http.headers定义 header 操作规则,包括 request 和 response header 的增删改。spec.tcp定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于 TCP 流量的路由规则,该规则会应用于任何非 HTTP 和 TLS 的端口。spec.tcp.match定义路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.tcp.route定义 TCP 连接转发的目的端。spec.tls定义一组有序的(优先匹配靠前的路由规则)应用于未终止的 TLS 或 HTTPS 流量的路由规则,该路由规则会应用于网格内部的 service 端口命名为 https-,tls- 开头的流量,来自 gateway 的端口协议为 HTTPS,TLS 的未终止加密流量,ServiceEntry 使用 HTTPS,TLS 协议的端口,当 https-,tls- 端口未关联 VirtualService 规则时将会被视为 TCP 流量。spec.tls.match定义 TLS 流量路由的匹配规则列表,单个匹配规则项内所有条件是且关系,多个匹配规则之间为或关系。spec.tls.route定义连接转发的目的端2.1 routeHTTP Route 规则的功能:满足 HTTPMatchRequest 条件的流量都会被路由到 HTTPRouteDestination,执行重定向(HTTPRedirect)、重写(HTTPRewrite)、重试(HTTPRetry)、故障注入(HTTPFaultInjection)、跨站(CorsPolicy)等策略。2.2 matchmatch 是路由的匹配规则,支持 uri、scheme、method、authority 等字段,且支持 perfix(前缀)、exact(精确)、regex(正则)三种匹配模式:# 匹配 uri 以 test 开头的请求 - match: - uri: prefix: "/test"# 匹配 header 中 key 为 source,value 为 abc 的请求 - match: - headers: source: exact: abc# 根据来源标签匹配 - match: sourceLabels: app: nginx version: v1# 匹配 header 中 key 为 source,value 为 test1 的请求 或 uri 以 test2 开头的请求 - match: - headers: source: exact: abc uri: prefix: "/test1" - uri: prefix: "/test2"2.3 路由目标(RouteDestionation)在 HTTPRouteDestionation 中主要包含三个字段:destination(请求目标)、weight(权重)、headers(请求头),其中 destination 必填。destination:通过 host、subset 和 port 三个属性描述,表示最终将流量路由到此目标。host 是 Destination 必选字段,表示在 lstio 中注册的服务名(建议写全域名),subset 表示在 host 上定义的一个子集,如:在灰度发布中将版本定义为 subset,配置路由策略会将流量转发到不同版本的 subset 上。spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 destination: host: test.com subset : v2weight:表示流量分配的比例,在一个 route 下多个 destination 的 weight 总和要求是100(默认100,必填字段)。如:从原有的 v1 版本中切分 20% 的流量到 v2 版本,这也是灰度发布常用的一个流量策略,即不区分内容,平等的从总流量中切出一部分流量给新版本。spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 weight: 80 destination: host: test.com subset : v2 weight: 20headers:提供了对 HTTP header 的一种操作机制,可以修改一次 HTTP 请求中的Request 或 Response 的值,包含 request 和 response 两个字段。request:表示在发请求给目标地址时修改 Request 的 headerresponse:表示在返回应答时修改 Response 的 header对应的类型都是 HeaderOperations 类型,使用set、add、remove字段来定义对 Header 的操作set:使用map上的key和value覆盖 Request 和 Response 中对应的 Headeradd:追加map上的key和value到原有的 Headerremove:删除在列表中指定的 Header2.4 HTTP重定向(HTTPRedirect)HTTPRedirect 包含两个字段来表示重定向的目标:uri:替换 URL 中的 uri 部分authority:替换 URL 中的 authority 部分# 对 nginx 服务中,所有前缀为 test1 的请求都会被重定向到 new-test 的 /test/a1 地址 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - match: - uri: prefix: /test1 redirect: uri: /test/a1 authority: new-test.com2.5 HTTP重写(HTTPRewrite)通过 HTTP 重写可以在将请求转发给目标服务前修改 HTTP 请求中指定部分的内容,HTTP 重写对用户是不可见的(在服务端执行)HTTPRewrite 包含两个字段:uri:重写 URL 中的 uri 部分authority:重写 URL 中的 authority 部分和 HTTPRedirect 规则稍有不同的是,HTTPRedirect 的 uri 只能替换全部的 path,但 HTTPRewrite 的 uri 是可以重写前缀的,即匹配条件是前缀匹配,则只修改匹配到的前缀。# 将请求前缀中的 /test1 重写为 /test/a1 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - match: - uri: prefix: /test1 rewrite: uri: /test/a1 route: - destination: host: new-test2.6 HTTP重试(HTTPRetry)HTTPRetry 可以定义请求失败时的重试策略,包含三个字段:attempts:必选字段,定义重试的次数perTryTimeout:每次重试超时的时间,单位可以是 ms、s、m和hretryOn:进行重试的条件,多个条件时以逗号分隔5xx:在上游服务返回 5xx 应答码,或者在没有返回时重试gateway-error:类似于5xx异常,只对502、503和504应答码进行重试connect-failure:在链接上游服务失败时重试retriable-4xx:在上游服务返回可重试的4xx应答码时执行重试refused-stream:在上游服务使用 REFUSED_STREAM 错误码重置时执行重试cancelled:gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 cancelled 时执行重试deadline-exceeded:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 deadline-exceeded 时执行重试internal:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 internal 时执行重试resource-exhausted:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 resource-exhausted 时执行重试unavailable:在 gRPC 应答的 Header 中状态码是 unavailable 时执行重试apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com retries: attempts: 3 perTryTimeout: 5s retryOn: 5xx,connect-failure2.7 HTTP流量镜像(HTTPMirror)HTTP 流量镜像指的是将流量转发到原目标地址的同时将流量给另外一个目标地址镜像一份。把生产环境中的实际流量镜像一份到另外一个系统上,完全不会对生产系统产生影响,这里只是镜像了一份流量,数据面代理只需要关注原来转发的流量就可以,不用等待镜像目标地址的返回。apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 mirror: host: test.net subset: v22.8 HTTP故障注入(HTTPFaultInjection)HTTPFaultInjection 通过 delay 和 abort 设置延时和中止两种故障,分别表示 Proxy 延迟转发和终止 HTTP 请求。delay 包含以下两个字段:fixedDelay:必选,表示延迟时间,单位可以是毫秒,秒,分钟和小时,要求至少要大于1毫秒percentage:延时作用在多少比例的请求上# 让 1.5% 的请求延时 5s apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 fault: delay: fixedDelay: 5s percentage: value: 1.5abort 包含以下两个字段:httpStatus:必选,http 状态码percentage:终止故障作用在多少比例的请求上# 让 1.5% 的请求返回 500 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 fault: abort: httpStatus: 500 percentage: value: 1.52.9 HTTP跨域资源共享(CorsPolicy)在 VirtualService 中可以对满足条件的请求配置跨域资源共享,allowOrigin,allowMethods,allowHeader,exposeHeader,maxAge,allowCredentials,等都被转化为 Access-Control-* 的 Header。# 允许来自 new-test.com 的 GET 请求 apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: nginx namespace: test spec: hosts: - test.com http: - route: - destination: host: test.com subset: v1 corsPolicy: allowOrigin: - new-test.com allowMethod: - GET maxAge: 2d