1. 特征匹配
Brute-Force 蛮力匹配
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import cv2 %matplotlib inline img1 = cv2.imread('ysg.png') img2 = cv2.imread('ysg_1.png') sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create() kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img1, None) kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img2, None) # crossCheck表示两个特征点要相互匹配,即A中的第i个特征点与B中的第j个特征点最近,反之,B中的第j个特征点到A中的第i个特征点也是 # NORM_L2:归一化数组(欧几里得距离),不同特征计算方法该参数不同 bf = cv2.BFMatcher(crossCheck=True)
一对一匹配
matches = bf.match(des1, des2) matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x: x.distance) img3 = cv2.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches[:10], None, flags=2) plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img3, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) plt.show()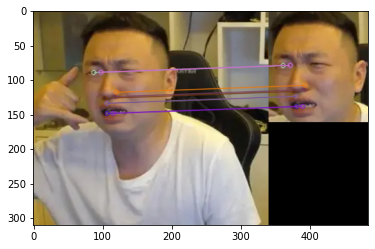
k对最佳匹配
bf = cv2.BFMatcher() matches = bf.knnMatch(des1, des2, k=2) good = [] for m, n in matches: if m.distance < 0.75 * n.distance: good.append([m]) img3 = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, good, None, flags=2) plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img3, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) plt.show()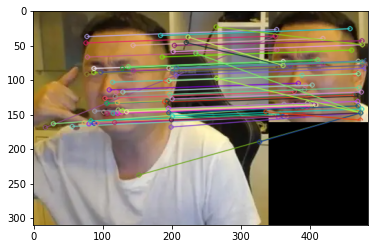
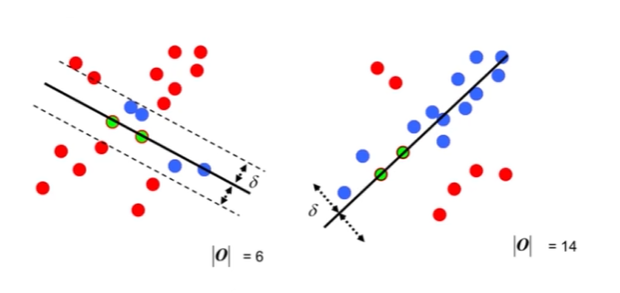
2. 随机抽样一致算法(Random sample consensus, RANSAC)
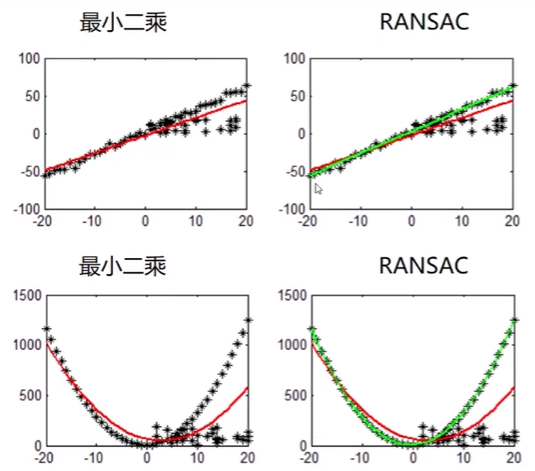
选择初始样本点进行拟合,给定一个容忍范围,不断进行迭代
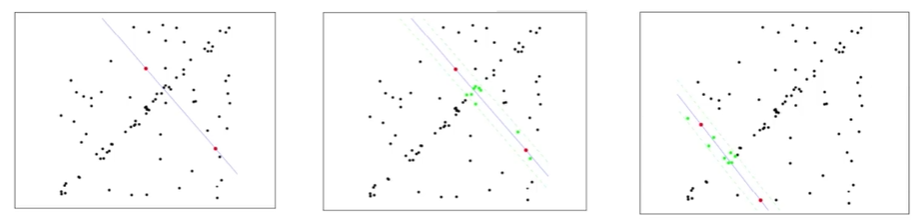
每一次拟合后,容差范围内都有对应的数据点数,找出数据点个数最多的情况,即可得到最终的拟合结果
单应性矩阵
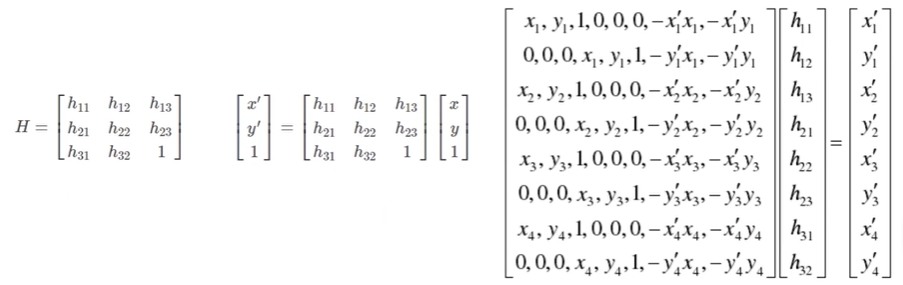
3. 演示
拼接 left right两张图片
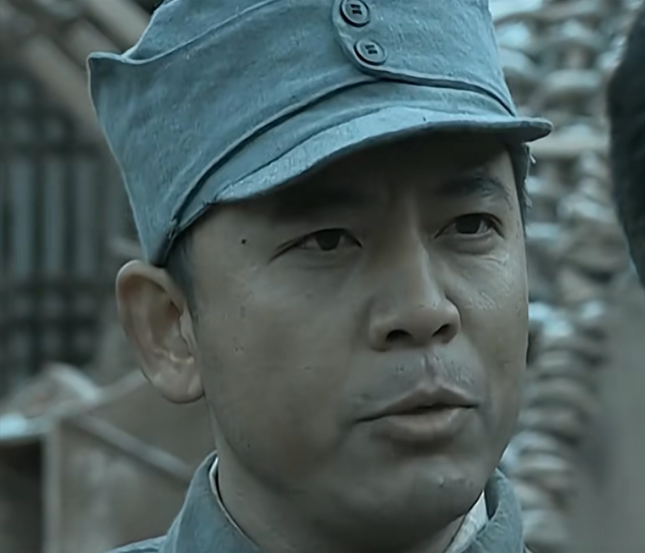
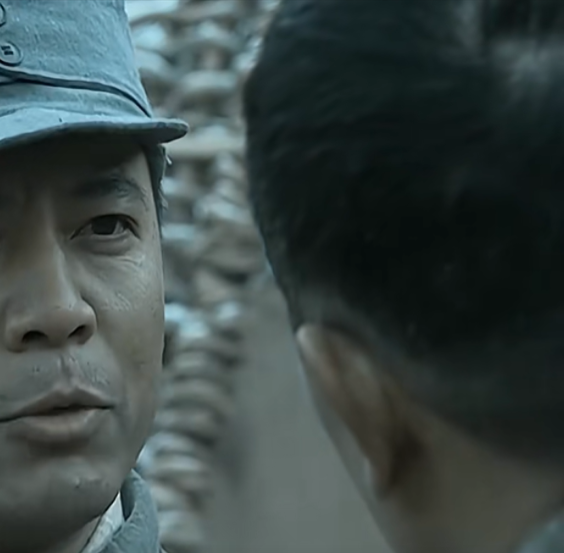


Stitcher.py
import numpy as np
import cv2
class Stitcher:
# 拼接函数
def stitch(self, images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0, showMatches=False):
(imageB, imageA) = images
# 检测图片A、B的sift关键特征点,并计算特征描述
(kpsA, featuresA) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, featuresB) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 匹配特征点
M = self.matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh)
if M is None:
return None
# 提取匹配结果 H 矩阵(3x3)
(matches, H, status) = M
# 图片A视角变换
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0]))
self.cv_show('resultA', result)
# 将图片B传入result最左边
result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB
self.cv_show('resultB', result)
if showMatches:
vis = self.drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
return (result, vis)
return result
def cv_show(self, title, img):
cv2.imshow(title, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def detectAndDescribe(self, image):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None)
# 结果转为Numpy数组
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps])
# 返回特征点集、描述特征
return (kps, features)
def matchKeypoints(self, kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh):
# 暴力匹配
matcher = cv2.BFMatcher()
# 使用KNN检测来自图片A、B的sift特征匹配对,k=2
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
# 当最近距离和次近距离的比值小于ratio时,保留此匹配对
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio:
matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
# 最少需要4对匹配对
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
# 计算视觉变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
return (matches, H, status)
return None
def drawMatches(self, imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
# 初始化可视化图片,将A、B左右连接到一起
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA
vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB
# 联合遍历,画出匹配对
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
# 当点对匹配成功时,执行画出
if s == 1:
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][9]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][10]))
cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
return vis
imgStitching.py
from Stitcher import Stitcher
import cv2
imageA = cv2.imread("images/left.png")
imageB = cv2.imread("images/right.png")
# 拼接
stitcher = Stitcher()
(result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([imageA, imageB], showMatches=True)
cv2.imshow("imageA", imageA)
cv2.imshow("imageB", imageB)
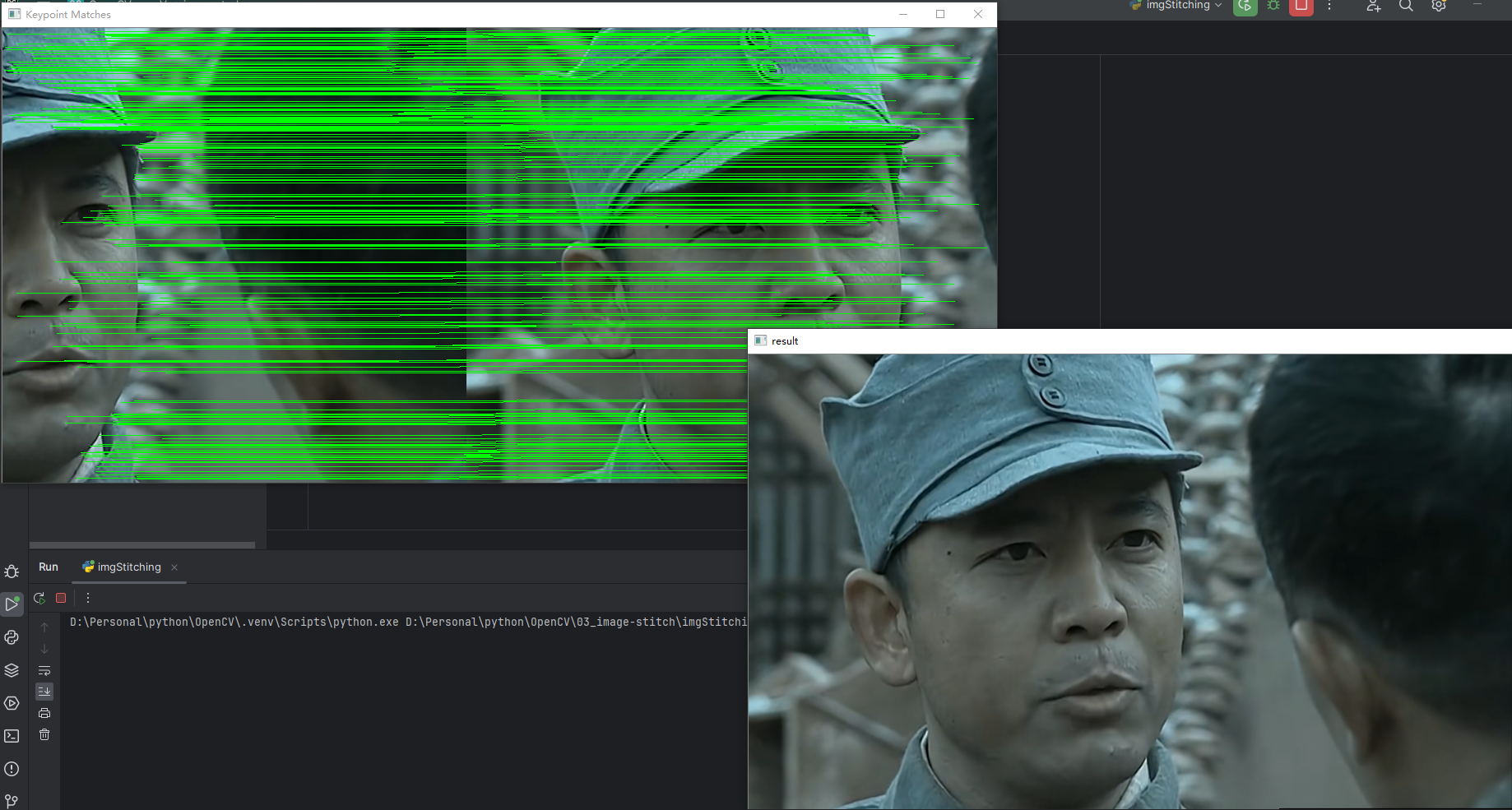
cv2.imshow("Keypoint Matches", vis)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
拼接结果


评论 (0)