(1)概述
提供一个对象来顺序访问聚合对象中的一系列数据,而不暴露内部对象的表示
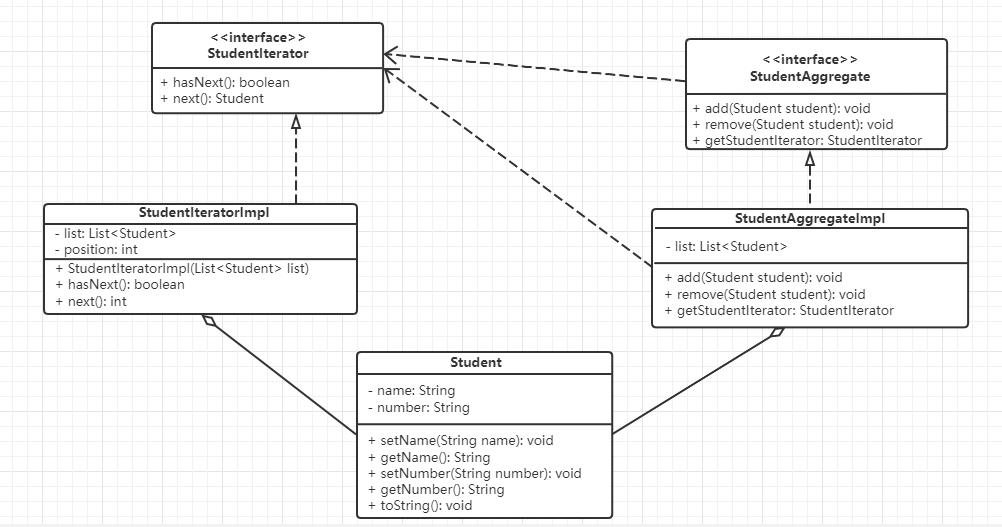
(2)结构
- 抽象聚合角色:定义存储、添加、删除聚合元素以及创建迭代器对象的接口
- 具体聚合角色:实现抽象聚合类,返回一个具体迭代器的实例
- 抽象迭代器角色:定义访问和遍历聚合元素的接口,通常包含
hasNext()、next()等方法 - 具体迭代器角色:实现抽象迭代器接口中所定义的方法,完成对聚合对象的遍历,记录遍历的当前位置
(3)案例
以遍历学生对象集合为例
抽象聚合角色
public interface StudentAggregate {
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param student
*/
void add(Student student);
/**
* 移除元素
*
* @param student
*/
void remove(Student student);
/**
* 获取迭代器
*
* @return
*/
StudentIterator getStudentIterator();
}具体聚合角色
public class StudentAggregateImpl implements StudentAggregate {
private List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void add(Student student) {
list.add(student);
}
@Override
public void remove(Student student) {
list.remove(student);
}
@Override
public StudentIterator getStudentIterator() {
return new StudentIteratorImpl(list);
}
}抽象迭代器角色
public interface StudentIterator {
/**
* 判断是否还有元素
*
* @return
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* 获取下一个元素
*
* @return
*/
Student next();
}具体迭代器角色
public class StudentIteratorImpl implements StudentIterator {
private List<Student> list;
//记录遍历时的位置
private int position = 0;
public StudentIteratorImpl(List<Student> list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return position < list.size();
}
@Override
public Student next() {
Student currentStudent = list.get(position);
position++;
return currentStudent;
}
}Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建聚合对象
StudentAggregateImpl studentAggregate = new StudentAggregateImpl();
//添加元素
studentAggregate.add(new Student("孙笑川", "001"));
studentAggregate.add(new Student("药水哥", "002"));
studentAggregate.add(new Student("刘波", "003"));
//获取迭代器对象
StudentIterator iterator = studentAggregate.getStudentIterator();
//遍历
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}(4)优缺点
- 支持以不同的方式遍历一个聚合对象,在同一个聚合对象上可以定义多种遍历方式,在迭代器模式中只需要用一个不同的迭代器来替换原有的迭代器即可改变遍历算法
- 简化了聚合类,在原有的聚合类中不需要再自行提供遍历等方法
- 由于引入了抽象层,新增新的聚合类和迭代器类都很方便,满足开闭原则
(5)使用场景
- 当需要为聚合对象提供多种遍历方式时
- 当需要为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口时
- 当需要访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露其内部细节时

评论 (0)