(1)概述
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类能一起工作,分为类适配器模式(耦合度高)和对象适配器模式
(2)结构
- 目标接口:当前系统业务所期待的接口(抽象类或接口)
- 适配者类:它是被访问和适配的现存组件库中的组件接口
- 适配器类:它是一个转换器,通过继承或引用适配者的对象,把适配者接口转换成目标接口,让客户按目标接口的格式访问适配者
(3)类适配器模式
实现方式:定义一个适配器类来实现当前系统的业务接口(即目标接口),同时又继承现有组件库中已经存在的组件(即适配者类)
以读卡器为例:
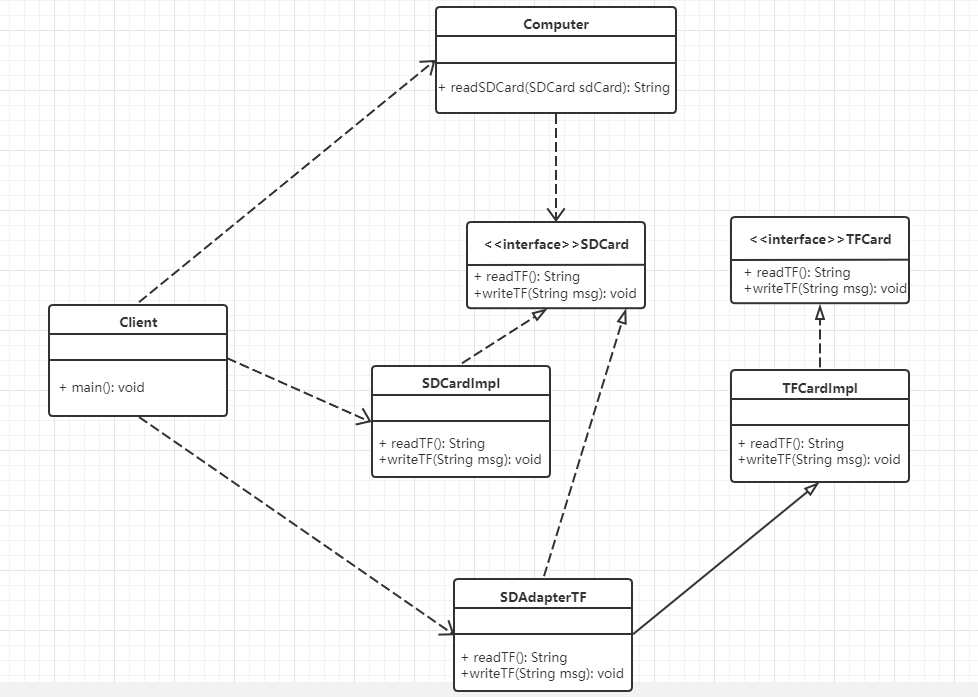
目标接口
public interface SDCard {
/**
* 读数据
*
* @return
*/
String readSD();
/**
* 写数据
*
* @param msg
*/
void writeSD(String msg);
}具体的SD卡类
public class SDCardImpl implements SDCard {
@Override
public String readSD() {
return "Read data from SDCard: Hello World";
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("Write data to SDCard:" + msg);
}
}public class Computer {
public String readSD(SDCard sdCard) {
if (sdCard == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("SDCard can not be null");
}
return sdCard.readSD();
}
}适配者类接口
public interface TFCard {
/**
* 读数据
*
* @return
*/
String readTF();
/**
* 写数据
*
* @param msg
*/
void writeTF(String msg);
}适配者类
public class TFCardImpl implements TFCard {
@Override
public String readTF() {
return "Read data from TFCard: Hello World";
}
@Override
public void writeTF(String msg) {
System.out.println("Write data to TFCard:" + msg);
}
}适配器类
public class SDAdapterTF extends TFCardImpl implements SDCard {
@Override
public String readSD() {
System.out.println("Adapter read from TFCard");
return super.readTF();
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("Adapter write to TFCard");
super.writeTF(msg);
}
}测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算机
Computer computer = new Computer();
//读取SDCard中的数据
String msg = computer.readSD(new SDCardImpl());
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println("====================================");
//使用该电脑读取TFCard中的数据
//定义适配器类
String msg1 = computer.readSD(new SDAdapterTF());
System.out.println(msg1);
}
}类适配器模式违背了合成复用原则,在客户类有一个明确的接口规范的情况下可用,反之不可用
(4)对象适配器模式
实现方式:采用将现有组件库中已实现的组件引入适配器类中,该类同时实现当前系统的业务接口
读卡器案例改进:
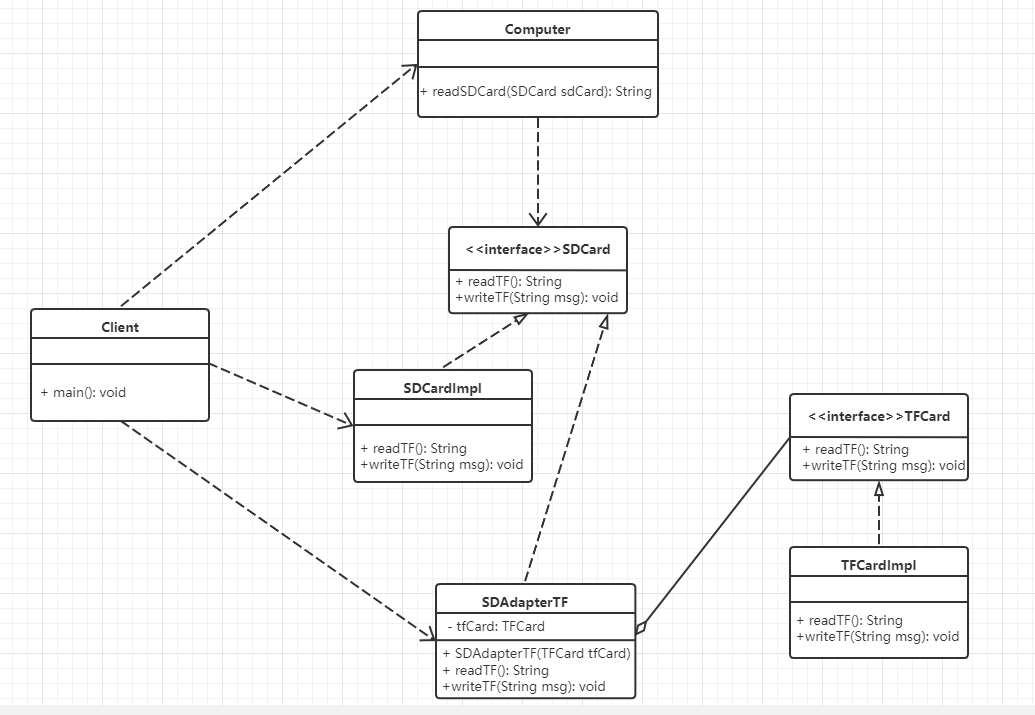
目标接口
public interface SDCard {
/**
* 读数据
*
* @return
*/
String readSD();
/**
* 写数据
*
* @param msg
*/
void writeSD(String msg);
}具体的SD卡类
public class SDCardImpl implements SDCard {
@Override
public String readSD() {
return "Read data from SDCard: Hello World";
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("Write data to SDCard:" + msg);
}
}public class Computer {
public String readSD(SDCard sdCard) {
if (sdCard == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("SDCard can not be null");
}
return sdCard.readSD();
}
}适配者类接口
public interface TFCard {
/**
* 读数据
*
* @return
*/
String readTF();
/**
* 写数据
*
* @param msg
*/
void writeTF(String msg);
}适配者类
public class TFCardImpl implements TFCard {
@Override
public String readTF() {
return "Read data from TFCard: Hello World";
}
@Override
public void writeTF(String msg) {
System.out.println("Write data to TFCard:" + msg);
}
}适配器类
public class SDAdapterTF implements SDCard {
//适配者类
private TFCard tfCard;
public SDAdapterTF(TFCard tfCard) {
this.tfCard = tfCard;
}
@Override
public String readSD() {
System.out.println("Adapter read from TFCard");
return tfCard.readTF();
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("Adapter write to TFCard");
tfCard.writeTF(msg);
}
}测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算机
Computer computer = new Computer();
//读取SDCard中的数据
String msg = computer.readSD(new SDCardImpl());
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println("====================================");
//使用该电脑读取TFCard中的数据
String msg1 = computer.readSD(new SDAdapterTF(new TFCardImpl()));
System.out.println(msg1);
}
}对象适配器模式解决了类适配器模式中存在的问题;同时还有接口适配器模式,当不希望实现一个接口中的所有方法时,可以定义一个 Adapter 抽象类,实现目标接口中的所有方法,适配器类再继承该抽象类,根据需要选择所需的方法
(5)应用场景
- 原系统存在满足新系统功能需求的类,但存在接口不一致的问题时
- 使用第三方提供的组件,但所需组件接口与自己接口定义不同的时候

评论 (0)