生产者和消费者问题
package com.sw.pc;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2021/1/4 14:25
*/
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
}
}
class Data{
private int num = 0;
//+1
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
if (num!=0){
//等待
this.wait();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
//-1
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
if (num==0){
//等待
this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
当增加多个线程时(A,B,C,D),会出现虚假唤醒的问题
虚假唤醒:线程可以被唤醒,但不会被通知、中断或超时
解决方法:将if判断换为while

package com.sw.pc;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2021/1/4 14:25
*/
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"C").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"D").start();
}
}
class Data{
private int num = 0;
//+1
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
while (num!=0){
//等待
this.wait();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
//-1
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
while (num==0){
//等待
this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
JUC版生产者消费者问题
使用了Condition接口下的await()等待和signalAll()通知
package com.sw.pc;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2021/1/4 14:55
*/
public class B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data1 data1 = new Data1();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data1.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data1.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data1.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"C").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data1.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"D").start();
}
}
class Data1{
private int num = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
//+1
public void incr() throws InterruptedException {
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
while (num!=0){
//等待
condition.await();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
//-1
public void decr() throws InterruptedException {
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
while (num==0){
//等待
condition.await();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>"+num);
//通知
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
}Condition精准通知与线程唤醒
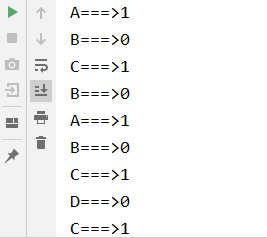
可以看到之前的线程执行顺序是无序的。
package com.sw.pc;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2021/1/4 15:08
* Condition精准通知与线程唤醒
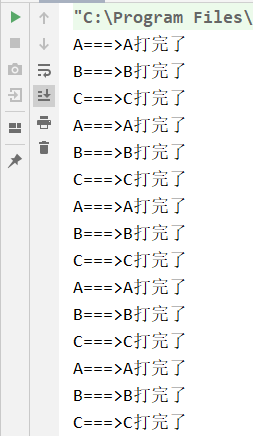
* ABC三个人互相打电话,A->B,B->C,C->A顺序执行
*/
public class C {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data2 data2 = new Data2();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data2.CallA();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data2.CallB();
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data2.CallC();
}
},"C").start();
}
}
class Data2{
private int num = 1; // 1A 2B 3C
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
public void CallA(){
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
while (num!=1){
//等待
condition1.await();
}
num = 2;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>A打完了");
//通知
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
public void CallB(){
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
while (num!=2){
//等待
condition2.await();
}
num = 3;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>B打完了");
//通知
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
public void CallC(){
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
while (num!=3){
//等待
condition3.await();
}
num = 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>C打完了");
//通知
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
}
通过不同的监视器监视线程来达到精准通知与线程唤醒的目的

评论 (0)