依赖注入
1、构造器注入
参考IoC创建对象的方式
2、Set方式注入
依赖注入:Set注入
- 依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
- 注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入
环境搭建:
1、复杂类型
package com.sw.pojo;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2020/12/14 16:32
*/
public class Adress {
private String adress;
public String getAdress() {
return adress;
}
public void setAdress(String adress) {
this.adress = adress;
}
}
2、真实测试对象
package com.sw.pojo;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2020/12/14 16:32
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Adress adress;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info;
……
}
3、beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.sw.pojo.Student">
<!--普通值注入 value-->
<property name="name" value="孙笑川"/>
</bean>
</beans>4、测试类
import com.sw.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author suaxi
* @Date 2020/12/14 16:38
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
beans.xml补充:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.sw.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="昆明"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.sw.pojo.Student">
<!--普通值注入 value-->
<property name="name" value="孙笑川"/>
<!--bean注入 ref-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--数组-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>高数一</value>
<value>英语一</value>
<value>毛概</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>跑步</value>
<value>游泳</value>
<value>听音乐</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份证" value="12345678"/>
<entry key="银行卡" value="87654321"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--set-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOL</value>
<value>FF14</value>
<value>CSGO</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--null-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!--properties-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="姓名">孙笑川</prop>
<prop key="学号">123</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>3、拓展方式注入
可以使用p命名空间和c命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--p命名空间注入,可以直接注入属性的值:property-->
<bean id="user" class="com.sw.pojo.User" p:id="1" p:name="孙笑川"/>
<!--c命名空间注入,通过构造器注入constructor-args-->
<bean id="user1" class="com.sw.pojo.User" c:id="2" c:name="刘波"/>
</beans>注:使用前需导入xml约束
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"4、bean的作用域
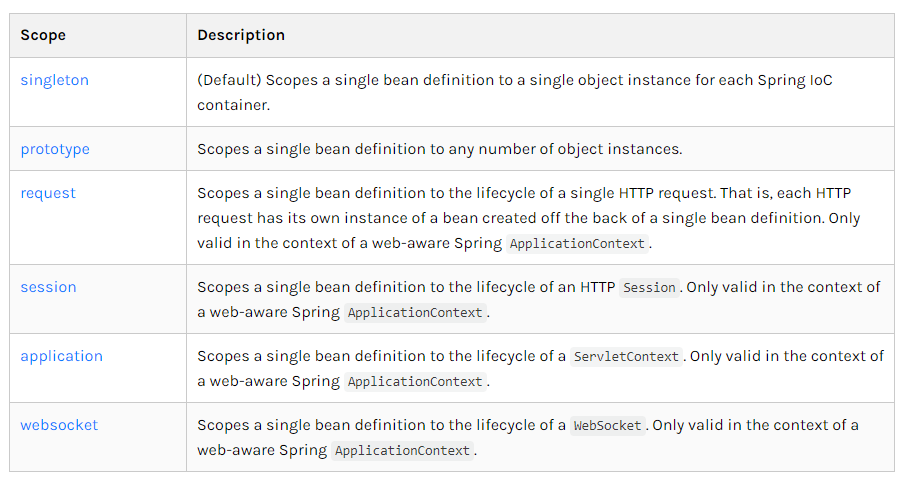
1、单例模式(Spring默认)
<bean id="user1" class="com.sw.pojo.User" c:id="2" c:name="刘波" scope="singleton"/>@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("userBeans.xml");
User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user");
User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user1==user2); //true
}2、原型模式:每次从容器中get的时候都会产生一个新对象
<bean id="user1" class="com.sw.pojo.User" c:id="2" c:name="刘波" scope="prototype"/>@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("userBeans.xml");
User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user1");
User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(user1.hashCode()); //838411509
System.out.println(user2.hashCode()); //1434041222
System.out.println(user1==user2); //false
}3、其余的request、session、application在web开发中使用





评论 (0)