1. 图像阈值
ret, dst = cv2.threshold(src, thresh, maxval, type)参数说明:
- src:输入图(只能输入单通道图像,一般为灰度图)
- dst:输出图
- thresh:阈值
- maxval:当像素值大于/小于阈值(根据type决定大于/小于),所赋予的值
type:二值化的操作类型,包含以下5种:
- cv2.THRESH_BINARY:超过阈值部分取maxval,否则取0
- cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV:THRESH_BINARY取反
- cv2.THRESH_TRUNC:大于阈值的像素值设为阈值,其他的不变
- cv2.THRESH_TOZERO:大于阈值的像素值不变,其他的设为0
- cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV:THRESH_TOZERO取反
import cv2 # OpenCV 读取的格式是 BGR
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
img = cv2.imread('ble.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.imread('ble.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ret, thresh3 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TRUNC)
ret, thresh4 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
ret, thresh5 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
titles = ['original', 'BINARY', 'BINARY_INV', 'TRUNC', 'TOZERO', 'TOZERO_INV']
images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5]
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1), plt.imshow(images[i], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()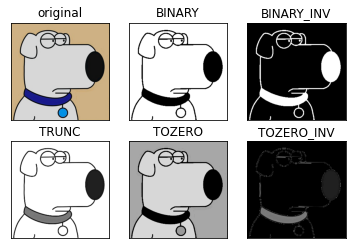
2. 图像平滑
img = cv2.imread('ysg.png')
# cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a857fb4d68>

# 均值滤波(平卷积操作)
blur = cv2.blur(img, (5, 5))
# cv2.imshow('blur', blur)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(blur, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a8592e8c50>

# 方框滤波
# normalize=True 即选择归一化时和均值滤波一样
box_normalize_true = cv2.boxFilter(img, -1, (5, 5), normalize=True)
# cv2.imshow('box_normalize_true', box_normalize_true)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(box_normalize_true, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a8592532b0>

# normalize=False 不做归一化,矩阵中的像素值相加,超过255取255
box_normalize_false = cv2.boxFilter(img, -1, (5, 5), normalize=False)
# cv2.imshow('box_normalize_false', box_normalize_false)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(box_normalize_false, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a8579eed30>

# 高斯滤波
gaussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 1)
# cv2.imshow('gaussian', gaussian)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(gaussian, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a857a7b828>

# 中值滤波
median = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
# cv2.imshow('median', median)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(median, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x2a8579d0588>



评论 (0)